Businesses in Canada Can Easily Find Bank Transit, Institution and Routing Numbers
Are you making payments from or to a Canadian bank account and need to find your transit, institution and routing numbers? Use Float’s free tools to locate the right credentials.
Pro Tip: Sign up for Float to never worry about confusing bank terminology and seamlessly send money via EFT, ACH and wire transfers.
Understanding Your Transit Number
What is an institution number?
An institution number is a unique three-digit code used by Canadian banks and financial institutions to identify themselves in the national financial system.
What is the account number?
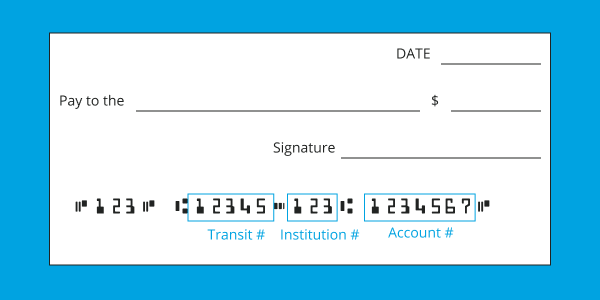
The account number on a cheque is a unique number assigned to an individual’s bank account, used to identify that specific account for financial transactions such as deposits, withdrawals, and transfers. It is typically found at the bottom of a cheque, following the transit number and institution number.
What is a transit number?
A transit number in Canadian banking is a five-digit code used to identify the specific branch of a financial institution where a bank account is held. It is part of the essential information needed for processing electronic funds transfers, direct deposits, and bill payments.
What is a routing number?
In Canada, a routing number is a combination of a transit number and an institution number that uniquely identifies a specific bank branch. It is used to facilitate financial transactions such as direct deposits, electronic fund transfers (EFTs), and wire transfers.
The Canadian routing number format is a 9-digit code that starts with a zero and then can be broken down into two main parts:
- Transit number: A 5-digit number that identifies the specific branch of a bank.
- Institution number: A 3-digit number that identifies the financial institution (e.g., Royal Bank of Canada’s institution number is 003).
The format for a Canadian routing number is typically 0YYYXXXXX, where:
0is a leading zero,YYYis the institution number, andXXXXXis the transit number.
For example, if the transit number is 12345 and the institution number is 003 (RBC), the routing number would be 000312345.
Find Credentials For Your Bank
Choose your bank below to lookup the Institution, Transit, Routing numbers and SWIFT codes for your bank
Bank Transit Number FAQ
In Canada, transit, institution and routing numbers are all used together for processing electronic transactions such as direct deposits, bill payments and wire transfers. The transit number identifies the specific bank branch, the institution number identifies the financial institution, and the routing number is a combination of both.
To send money in Canada from your bank account, you can use options like Interac e-transfer for fast transfers via email, EFT (Electronic Funds Transfer) for direct payments or a wire transfer for larger transactions. But, if you get frustrated with slow, manual and error prone bank portals, you can always consider using Float’s Bill Pay product—it’s free. Yes, actually.
An IBAN (International Bank Account Number) is a standardized format used to identify bank accounts internationally, ensuring smooth cross-border transactions. It includes the country code, cheque digits, and local bank account details. A SWIFT code (or BIC – Bank Identifier Code) is an 8 to 11 character code that identifies a specific bank during international transfers. The IBAN identifies the individual account, while the SWIFT code identifies the bank.
Both are required when sending money abroad and most often for WIRE transfers: the IBAN is used in regions like Europe, while the SWIFT code is used globally to identify the recipient’s bank for secure international transfers.
A Bank Identifier Code (BIC), also known as a SWIFT code, is an 8 to 11 character code used to uniquely identify banks and financial institutions worldwide for international transactions. It ensures that payments reach the correct institution. The code typically consists of the bank’s name, country, location and optional branch identifier. BIC codes are essential for wire transfers, international money transfers and other secure communication between banks globally.
ACH (Automated Clearing House) is a type of bank-to-bank payment method used in the U.S. for transactions like direct deposits and bill payments, processing batch payments between banks. In Canada, EFT refers to similar electronic money transfers, such as payroll deposits or vendor payments, across Canadian banks. TLDR? ACH refers to U.S.-specific transfers, while EFT is used in Canada.